Overview
- Introduction: When Is Dog Diarrhea An Emergency
- The Concerning Pet's Symptoms: Dog Diarrhea
- The Importance of Timely Action: Initial Treatment
- Understanding Dog Diarrhea
- Recognizing Emergency Signs: Diarrhea in Dogs
- At-Home First Aid for Managing Dog's Diarrhea
- When to Consult a Veterinarian: Ensuring Your Dog's Well-being
- Diagnostic Procedures: Treat Diarrhea
- Treatment Options for Diarrhea in Dogs: Tailoring Care to the Cause
- Home Care During Recovery: Nurturing Your Dog Back to Health
- Preventing Future Episodes
- Diarrhea in Puppies and Elderly Dogs: Tailoring Care for Different Life Stages
- Food Allergies and Sensitivities
- When Diarrhea May Indicate a Chronic Condition
- The Role of Diet in Managing Diarrhea
- Summary of Emergency Indicators
- FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- Conclusion: Educate Pet Owners
Introduction: When Is Dog Diarrhea An Emergency
As responsible pet owners, we all want our furry companions to lead happy and healthy lives. However, when it comes to our beloved dogs, health concerns can arise unexpectedly.
One common issue that often causes concern is diarrhea. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of dog diarrhea, specifically focusing on when it should be considered an emergency.
The Concerning Pet’s Symptoms: Dog Diarrhea
Dog diarrhea is a concerning symptom for pet owners. It’s essential to understand that while occasional bouts of loose stool may not be a cause for immediate alarm, persistent or severe diarrhea can indicate an underlying issue that requires urgent attention.
The Importance of Timely Action: Initial Treatment
Timely action is crucial when it comes to your dog’s health. Ignoring diarrhea or delaying treatment can lead to complications and worsen your pet’s condition. Therefore, it’s vital to decode the signs and know when to seek immediate veterinary care.
Understanding Dog Diarrhea
Understanding the basics of dog diarrhea is the first step in deciphering whether it’s an emergency or not.
Normal vs. Abnormal Stools
Before panicking over a loose stool, it’s essential to know what’s normal for your dog. Stool consistency can vary between breeds and individuals. Differentiating between normal and abnormal stools is key to identifying potential problems.
Causes of Dog’s Diarrhea
- Dietary Factors: Diet plays a significant role in a dog’s digestive health. Sudden changes in food, dietary indiscretions like eating garbage, or the introduction of new treats can trigger diarrhea.
- Bacterial Infections: Bacterial infections in the gastrointestinal tract can lead to acute diarrhea. Common culprits include Salmonella and E. coli.
- Parasitic Infections: Intestinal parasites like worms and Giardia can cause persistent diarrhea if left untreated.
- Viral Infections: Viruses such as Parvovirus can lead to severe and often bloody diarrhea, especially in puppies.
- Stress and Anxiety: Dogs can experience stress-induced diarrhea, especially in unfamiliar or anxiety-inducing situations.
- Medications: Some medications, such as antibiotics, can disrupt the balance of the gut flora and result in diarrhea.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Chronic conditions like kidney disease and inflammatory bowel disease can manifest as chronic diarrhea.

Recognizing Emergency Signs: Diarrhea in Dogs
Dog diarrhea is a common issue that many dog owners encounter, but not all cases require immediate action. Understanding when dog diarrhea becomes an emergency is essential to ensure your furry friend’s health. Here are some key indicators to watch for:
Persistent Diarrhea: When your dog experiences diarrhea for an extended period, lasting more than 24 hours, it’s time to consult a veterinarian. Persistent diarrhea can be a sign of chronic conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease or dietary indiscretion.
Blood in Stools: The presence of blood in your dog’s stool is a serious concern and warrants immediate attention. Blood can be a sign of various underlying issues, including infections, gastrointestinal bleeding, or even a foreign object in the digestive tract.
Dehydration: Dehydration is a common complication of diarrhea and can escalate quickly, especially in severe cases. Signs of dehydration include sticky gums, sunken eyes, and lethargy. Dehydrated dogs need immediate fluid replacement to avoid further health complications.
Weakness and Lethargy: If your dog becomes weak or lethargic in conjunction with diarrhea, it could be a sign that the diarrhea is taking a toll on their overall health. Weakness may indicate a compromised immune system or severe gastrointestinal distress.
Frequent Vomiting: Vomiting alongside diarrhea can lead to rapid fluid loss and should not be taken lightly. Frequent vomiting may indicate a more serious issue in your dog’s gastrointestinal tract, and it’s crucial to seek veterinary care promptly.
In cases where these emergency signs are present, it’s advisable to contact your nearest emergency animal hospital or your regular veterinarian immediately. Quick action can make a significant difference in your dog’s recovery and well-being.
To prevent such emergencies, consider feeding your dog specially formulated dog foods that cater to their specific dietary needs. Inflammatory bowel disease and chronic diarrhea can often be managed with a bland diet, such as boiled chicken and plain cooked white rice, as recommended by your veterinarian.

At-Home First Aid for Managing Dog’s Diarrhea
When your furry companion experiences mild diarrhea, it can be concerning, but there are steps you can take at home to provide comfort and support. While these measures are not a substitute for veterinary care, they can help alleviate your dog’s discomfort:
Assessing the Situation: Begin by evaluating your dog’s overall condition. Take note of any other symptoms they may be experiencing, such as abdominal pain, changes in appetite, or behavioral changes. Understanding the full picture of your dog’s health can assist your veterinarian in making an accurate diagnosis.
Managing Mild Diarrhea: One effective way to manage mild diarrhea in dogs is by offering a bland diet. Boiled chicken and plain cooked white rice can be soothing to your dog’s upset tummy. These ingredients are gentle on the digestive tract and can help firm up loose stools. Ensure that the chicken is thoroughly cooked and free from any seasonings or additives.
Hydration Strategies: Maintaining proper hydration is crucial when your dog has diarrhea. Make sure your dog has access to clean, fresh water at all times. Dehydration can worsen diarrhea and lead to more severe health issues. In some cases, you can also offer ice cubes or ice chips to entice your dog to drink more fluids.
While these home remedies can be helpful for mild cases of diarrhea, it’s essential to keep an eye on your dog’s condition. If the diarrhea persists or worsens, it’s time to seek veterinary attention. Remember that over-the-counter medications meant for humans should not be given to dogs without the guidance of a veterinary professional, as they can have adverse effects.

When to Consult a Veterinarian: Ensuring Your Dog’s Well-being
Recognizing when to seek professional help for your dog’s diarrhea is of utmost importance in safeguarding their health and well-being. Here are some crucial steps to follow:
Contacting the Vet: If you find yourself uncertain about the severity of your dog’s diarrhea or if it persists beyond a day, it’s advisable to promptly contact your veterinarian. Veterinarians are trained to assess the situation and provide guidance based on their expertise. It’s better to err on the side of caution and seek professional advice.
Providing Critical Information: When reaching out to your veterinarian, be prepared to provide essential information about your dog’s condition. This includes details about the onset and duration of diarrhea, any accompanying symptoms such as vomiting or lethargy, recent changes in your dog’s diet or routine, and any medications your dog may be taking. Clear communication enables the vet to make a more accurate assessment of your dog’s condition.
Scheduled vs. Emergency Visit: Your veterinarian will help you determine whether your dog’s situation necessitates an emergency visit or if a scheduled appointment is appropriate. Emergency visits are crucial when there are severe symptoms such as bloody diarrhea, signs of dehydration, abdominal pain, or other critical indicators. In such cases, immediate attention can be life-saving. For less severe or non-urgent cases, your vet may schedule a regular appointment to conduct a thorough examination and diagnostic tests as needed.
Understanding the urgency of the situation is vital, as some symptoms can be indicative of very serious health issues, such as kidney disease, gastrointestinal blockage, or acute infections. Timely intervention is often the key to successful treatment and a faster recovery.
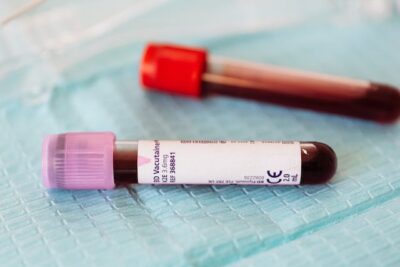
Diagnostic Procedures: Treat Diarrhea
When your dog’s diarrhea persists despite home care efforts or when concerning signs are present, your veterinarian may recommend diagnostic tests to uncover the underlying causes.
These diagnostic procedures are instrumental in identifying the root of the issue:
Fecal Examination: A fecal examination is a common diagnostic tool used to detect the presence of parasites or bacterial infections in your dog’s digestive system. By analyzing a stool sample, your veterinarian can pinpoint the specific culprits responsible for your dog’s diarrhea. This information guides treatment decisions, ensuring targeted and effective solutions.
Blood Tests: Blood work offers valuable insights into your dog’s overall health and can reveal underlying conditions contributing to the diarrhea. Abnormalities in blood parameters may indicate kidney disease, infections, or other systemic issues. This comprehensive assessment helps your veterinarian formulate an appropriate treatment plan tailored to your dog’s specific needs.
Imaging: In cases where gastrointestinal blockages, abnormalities, or painful blockage is suspected, imaging techniques such as X-rays or ultrasound may be employed. These non-invasive procedures allow your veterinarian to visualize the gastrointestinal tract and identify any foreign objects, obstructions, or structural irregularities. This critical information guides treatment decisions and ensures a safe and effective approach.
Endoscopy and Biopsy: For complex cases that demand a deeper understanding of your dog’s condition, endoscopy and biopsy may be necessary. Endoscopy involves the insertion of a flexible tube with a camera into the digestive tract, allowing for a real-time examination of the gastrointestinal lining. Biopsies may be taken during this procedure to obtain tissue samples for further analysis. This in-depth evaluation aids in diagnosing conditions like inflammatory bowel disease and provides invaluable information for targeted treatment strategies.
Treatment Options for Diarrhea in Dogs: Tailoring Care to the Cause
The treatment for dog diarrhea is not one-size-fits-all, as it depends on the underlying cause. Your veterinarian will develop a customized treatment plan based on your dog’s specific condition:
Medications for Diarrhea: If your dog is experiencing diarrhea, your veterinarian may prescribe medications to alleviate the symptoms. These medications are designed to address the specific cause of the diarrhea, whether it’s due to infection, inflammation, or other factors contributing to gastrointestinal distress.
Antibiotics for Infections: Bacterial infections can be a common cause of diarrhea in dogs. In such cases, antibiotics may be recommended to target and eliminate the harmful bacteria responsible for the infection. Always follow your veterinarian’s instructions when administering antibiotics to your dog.
Fluid Therapy: In cases of severe dehydration resulting from diarrhea, your dog may require intravenous (IV) fluid therapy. This therapy helps rehydrate your dog and restore essential electrolyte balance, which is crucial for their overall health.
Dietary Changes: For dogs with chronic diarrhea or dietary sensitivities, switching to a specially formulated dog food may be advised. These specialized diets are gentle on the digestive tract and can help manage ongoing gastrointestinal issues. Discuss dietary options with your veterinarian to find the most suitable choice for your dog.
Managing Stress: Stress-induced diarrhea is not uncommon in dogs, especially during times of anxiety or major life changes. Implementing stress reduction techniques can be beneficial. Providing a calm and structured environment, regular exercise, and positive reinforcement training can help reduce stress and alleviate related digestive issues.
Product Recommendations: Consider using products like “Diarrhea D-Fender” and “Pup Shield’s Diarrhea D-Fender Beef-Flavored Gummy Chews for Dogs” from Pup Shield Products. These products are designed to support digestive health and can complement your dog’s treatment plan. Always consult with your veterinarian before adding supplements or products to your dog’s diet.

Home Care During Recovery: Nurturing Your Dog Back to Health
After your dog has received treatment for diarrhea, providing the right care at home is crucial to their recovery. Here are some essential steps to ensure your furry friend bounces back to their happy and healthy self:
Post-Treatment Care: Follow your veterinarian’s instructions diligently for post-treatment care. This may include administering prescribed medications, adhering to dietary recommendations, and monitoring your dog’s progress closely. Consistency and attention to detail are key to a successful recovery.
Dietary Adjustments: Gradually transition your dog back to their regular diet as recommended by your veterinarian. It’s essential to ease them back into their usual food to avoid any sudden digestive upsets. If a dietary change was part of the treatment plan, make this transition gradually to ensure your dog’s stomach adapts comfortably.
Monitoring Progress: Regularly monitor your dog’s progress during the recovery period. Keep a close eye on their overall condition, including their appetite, behavior, and bowel movements. Any changes or concerning symptoms should be promptly reported to your veterinarian. Open communication ensures that any issues can be addressed promptly.

Preventing Future Episodes
Ensuring your dog’s well-being goes beyond just treating diarrhea; it involves taking proactive steps to prevent future episodes and maintain their overall health. Here are some vital strategies to consider:
Dietary Modifications: If your dog has experienced food allergies or sensitivities that contributed to their diarrhea, consider dietary modifications. Consult with your veterinarian to identify potential triggers and explore suitable diet options that are gentle on your dog’s digestive system. Specially formulated dog foods may be recommended to address specific dietary needs.
Parasite Prevention: Regular parasite prevention is essential for maintaining a healthy gastrointestinal tract. Parasites such as worms can disrupt your dog’s digestive system and lead to diarrhea. Consult with your veterinarian to establish a parasite prevention plan tailored to your dog’s lifestyle and needs.
Stress Reduction Techniques: Stress-induced diarrhea is a common occurrence in dogs. Implementing stress reduction techniques can significantly minimize the risk of such episodes. Ensure your dog has a structured routine, engage in regular exercise and play, and create a calm and reassuring environment. Positive reinforcement training can also help reduce stress and anxiety.
Regular Vet Check-ups: Regular check-ups with your veterinarian are crucial for catching underlying health issues before they escalate into diarrhea or other serious conditions. Routine examinations, vaccinations, and screenings can help identify and address potential health concerns early, promoting your dog’s long-term well-being.
Remember that your role as a pet owner is vital in preventing future episodes of diarrhea. Be attentive to your dog’s behavior and any changes in their eating habits, stool consistency, or overall health. Open communication with your veterinarian ensures that you can address any concerns promptly and receive guidance on preventive measures.

Diarrhea in Puppies and Elderly Dogs: Tailoring Care for Different Life Stages
Dealing with diarrhea in puppies and elderly dogs requires special considerations, as these life stages come with their own unique needs and vulnerabilities.
Special Considerations: Both puppies and elderly dogs may require extra attention and care when it comes to managing diarrhea. Their developing or aging bodies may respond differently to treatment, making it crucial to tailor the approach to their specific needs.
Monitoring Young and Senior Dogs: Vigilance is key when monitoring the health of puppies and senior dogs. Here are some age-specific aspects to keep in mind:
Puppies:
- Rapid Growth: Puppies undergo rapid growth and development, which can affect their digestive system. Diarrhea in puppies can be more common due to dietary adjustments and exploring their environment.
- Sensitive Systems: Puppy digestive systems are often more sensitive. It’s important to provide them with a balanced, high-quality diet designed for their age and breed.
- Parasite Risk: Puppies are more susceptible to parasites, which can lead to diarrhea. Regular deworming and parasite prevention are essential.
Senior Dogs:
- Aging Digestive Tract: Senior dogs may experience changes in their digestive tract as they age. This can make them more prone to diarrhea and dietary sensitivities.
- Reduced Immunity: Aging dogs may have a compromised immune system, which can affect their ability to fight off infections that cause diarrhea.
- Underlying Health Issues: Seniors are more likely to have underlying health conditions, such as kidney disease or inflammatory bowel disease, which can contribute to diarrhea.
When dealing with diarrhea in puppies or elderly dogs, consult your veterinarian promptly. They can provide guidance on age-appropriate treatments, dietary adjustments, and monitoring to ensure the best possible outcome.

Food Allergies and Sensitivities
When it comes to managing your dog’s diarrhea, identifying the triggers for food allergies and sensitivities is essential. Here’s how you can take proactive steps:
Identifying Triggers:
- Observation: Start by closely observing your dog’s diet and digestive patterns. Look for recurring episodes of diarrhea and any common factors in their meals.
- Elimination Diet: Your veterinarian may recommend an elimination diet to pinpoint the specific ingredients that trigger your dog’s digestive upset. This process involves gradually introducing different ingredients while monitoring their reactions.
- Allergy Testing: In some cases, allergy testing may be conducted to identify specific food allergens that affect your dog.
Implementing Allergy-Appropriate Diets: Once you’ve identified the triggers for your dog’s food allergies or sensitivities, it’s crucial to make dietary changes to prevent future episodes of diarrhea. Here’s how:
- Switch to Allergy-Appropriate Diets: Consult with your veterinarian to select an allergy-appropriate diet for your dog. These diets are specially formulated to exclude the ingredients that your dog is sensitive to. They can provide the necessary nutrients while avoiding allergens.
- Gradual Transition: When transitioning to a new diet, do so gradually to minimize digestive upset. Gradual changes allow your dog’s stomach to adapt to the new food without causing diarrhea.
When Diarrhea May Indicate a Chronic Condition
While occasional bouts of diarrhea in dogs are common and often related to dietary indiscretion or mild intestinal distress, chronic diarrhea can be indicative of underlying chronic conditions that require specialized attention. Here are some chronic conditions associated with chronic diarrhea in dogs:
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Inflammatory bowel disease is a chronic gastrointestinal disorder characterized by inflammation of the digestive tract. Dogs with IBD may experience recurrent diarrhea, weight loss, and abdominal discomfort. Managing IBD often involves dietary modifications, medications, and close veterinary supervision.
Food Intolerances: Food intolerances occur when a dog’s digestive system has difficulty processing specific food components. These intolerances can lead to chronic diarrhea. Identifying and addressing trigger ingredients through an elimination diet is crucial for managing this condition.
Other Gastrointestinal Disorders: Numerous other gastrointestinal disorders can contribute to chronic diarrhea in dogs. These conditions may include gastroenteritis, colitis, malabsorption disorders, or infections. Accurate diagnosis through veterinary evaluation and diagnostic tests is essential to determine the underlying cause and establish an appropriate treatment plan.
If you suspect that your dog is suffering from chronic diarrhea, it’s imperative to seek professional veterinary care promptly. Chronic diarrhea can lead to dehydration, nutrient deficiencies, and a reduced quality of life for your furry friend. Your veterinarian will conduct a thorough evaluation, which may include blood work, imaging, or endoscopy, to pinpoint the exact cause of the chronic diarrhea.
The Role of Diet in Managing Diarrhea
When your beloved canine companion experiences diarrhea, their diet can play a crucial role in easing their discomfort and promoting a speedy recovery. Here’s how you can harness the power of the right diet:
Bland Diet Recommendations: A bland diet is often recommended to soothe your dog’s irritated digestive system during bouts of diarrhea. This diet consists of easily digestible foods that provide essential nutrients while minimizing stress on the gastrointestinal tract. A common bland diet includes boiled chicken and plain cooked white rice, as these ingredients are gentle on the stomach.
Gradual Transition to Regular Diet: As your dog’s condition improves and diarrhea subsides, it’s essential to reintroduce their regular food gradually. Abrupt dietary changes can trigger digestive upset, potentially leading to a recurrence of diarrhea. Slowly transition from the bland diet back to their usual food over several days or as advised by your veterinarian.

Summary of Emergency Indicators
In the world of pet ownership, being prepared can make all the difference when faced with a canine health emergency. Let’s summarize the critical aspects of recognizing and responding to emergency indicators in cases of dog diarrhea:
Recap of Red Flags: It’s essential to recognize the red flags that signal when diarrhea in your dog should be considered an emergency. These include persistent diarrhea lasting more than 24 hours, the presence of blood in stools, signs of dehydration such as sticky gums and sunken eyes, weakness or lethargy, and frequent vomiting when accompanied by diarrhea. If you observe any of these signs, it’s time to take prompt action to safeguard your dog’s health.
Quick Action Guide: To ensure you’re always prepared, it’s a good idea to have a quick action guide on hand for dog diarrhea emergencies. This guide should include steps to take in case of an emergency, such as contacting your veterinarian immediately or heading to the nearest emergency animal hospital. Be ready to provide critical information about your dog’s symptoms, diet, and any recent changes in their routine when communicating with your vet. Your quick action can make all the difference in ensuring the best possible outcome for your furry friend.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Let’s dive into some common questions pet owners often have about dog diarrhea:
What causes diarrhea in dogs?
- Diarrhea in dogs can stem from various factors, including dietary issues, infections, stress, and underlying health conditions.
When is diarrhea considered an emergency?
- Diarrhea should raise concerns when it persists for more than 24 hours, is accompanied by blood in the stool, or if it leads to severe dehydration.
Can I give my dog over-the-counter medications for diarrhea?
- It’s always advisable to consult your veterinarian before administering any medications to your dog. Some human medications can be harmful to them.
How can I tell if my dog is dehydrated?
- Signs of dehydration in dogs include having sticky gums, sunken eyes, displaying lethargy, and experiencing a loss of appetite.
Is it normal for a dog to have occasional diarrhea?
- Occasional bouts of diarrhea can be considered normal, but if your dog experiences persistent or severe diarrhea, it’s crucial to investigate the underlying causes.
Are certain dog breeds more prone to diarrhea?
- While some dog breeds may have more sensitive stomachs than others, diarrhea can affect any breed.
Can stress and anxiety trigger diarrhea in dogs?
- Yes, stress and anxiety can lead to stress-induced diarrhea in dogs, just as it can in humans.
How can I prevent my dog from getting diarrhea in the first place?
- Preventive measures include maintaining a consistent and balanced diet, scheduling regular veterinary check-ups, and minimizing stressors in your dog’s environment.
Are there any home remedies for mild cases of dog diarrhea?
- For mild cases, you can try feeding your dog a bland diet consisting of boiled chicken and plain cooked white rice. This can help soothe their digestive discomfort.
What should I expect during a vet visit for diarrhea?
- During a veterinary visit for diarrhea, your veterinarian will conduct a thorough examination, which may include diagnostic tests if necessary. Based on their findings, they will prescribe appropriate treatment to address the specific issue.
Conclusion: Educate Pet Owners
Your canine companion’s health is undeniably a top priority, and being well-informed about how to respond when faced with diarrhea can have a profound impact on their overall well-being. Always keep a watchful eye on your furry friend’s health and be ready to take swift action to ensure a happy and healthy pup.
Remember that diarrhea can sometimes be a sign of more severe underlying issues, such as foreign objects or fabric ingesting toxins, making it essential to educate fellow pet owners about recognizing the signs and symptoms. Whether you’re dealing with frequent bouts of diarrhea, ensuring that nursing puppies stay healthy, or simply maintaining your dog’s digestive system, understanding the nuances of your dog’s regular food and their GI tract is crucial.
In cases of mild digestive upset, consider incorporating natural yogurt and canned plain pumpkin to alleviate your dog’s discomfort. However, if the situation worsens or sudden diarrhea becomes a concern, especially in adult dogs or after experiencing two or more bouts, it’s crucial to acknowledge that this may indicate a severe health issue.
For further insights on proactive dog care and various topics beneficial for dog owners, explore our blog. Your attentiveness and proactive approach to your dog’s health can ultimately contribute to a happier and healthier life for your beloved four-legged family member.




